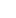
The press-fit mechanism allows the tee to be installed quickly and securely using a specialized tool that presses the components together. This eliminates the need for additional welding, threading, or sealing materials. The resulting connection is tight, durable, and resistant to leaks, making it ideal for both commercial and industrial systems.

Composition of Bronze
The primary material used in the construction of press fit bronze tees is bronze, an alloy consisting mainly of copper (Cu) and tin (Sn). The exact composition of bronze can vary, but the following are the key components typically found in industrial-grade bronze alloys:
1. Copper (Cu)
Copper is the primary component of bronze and typically makes up about 60-90% of the alloy by weight. Copper imparts several key properties to bronze, including:
Corrosion Resistance: Copper is naturally resistant to corrosion, especially in water and air. This makes bronze an ideal material for fittings that will be exposed to harsh environments, such as plumbing and marine systems.
Thermal and Electrical Conductivity: Copper has thermal and electrical conductivity, although this property is secondary in press fit bronze tees, where the focus is more on corrosion resistance and mechanical strength.
Ductility: Copper adds to the malleability and workability of the alloy, making it easier to manufacture bronze fittings and adapt them to various applications.
2. Tin (Sn)
Tin, usually making up 5-15% of the bronze alloy, contributes to several critical properties:
Improved Strength: Tin enhances the strength and hardness of the bronze alloy, making it more durable and resistant to wear. This is particularly important for components like press fit tees, which must withstand pressure and mechanical stresses.
Increased Corrosion Resistance: Tin further improves the alloy's ability to resist corrosion, particularly in acidic or saline environments. This is especially valuable for systems exposed to water, chemicals, or marine environments, where corrosion can otherwise significantly shorten the lifespan of the components.
Casting Ability: Tin improves the fluidity of molten bronze, which makes it easier to cast and mold into the desired shape. This helps ensure that press fit bronze tees are free from defects and have a smooth, precise finish.
3. Other Elements (Aluminum, Phosphorus, Lead)
In some bronze alloys, small amounts of other elements may be added to provide specific benefits:
Aluminum: Aluminum is often included in certain bronze alloys to increase strength and resistance to corrosion. It is particularly useful in applications requiring durability in harsh environmental conditions.
Phosphorus: Phosphorus is sometimes added to improve wear resistance, particularly in applications where the fitting will experience friction.
Lead: In small amounts, lead can be used to improve machinability, allowing the bronze tees to be easily fabricated and shaped during the manufacturing process. However, lead is less common in modern bronze alloys due to health and environmental concerns.
Advantages of Using Bronze for Press Fit Tee Fittings
The choice of bronze as the material for press fit tees offers numerous advantages that make it suitable for a wide range of applications:
1. Corrosion Resistance
One of the significant advantages of bronze is its resistance to corrosion, particularly in moist or wet environments. This resistance extends to common corrosive agents such as water, saltwater, and many acids. For example, bronze is highly resistant to corrosion in marine environments, making it an ideal material for use in ships, boats, and offshore applications. Its ability to withstand corrosion without deteriorating over time ensures that the press fit bronze tee will perform reliably for many years.
2. Strength and Durability
Bronze is known for its mechanical strength, making it capable of handling high-pressure systems without deforming or failing. The alloy is also highly resistant to fatigue and wear, which means that press fit bronze tees can withstand the stresses typically encountered in industrial and commercial plumbing systems. This durability is especially important in systems that operate under constant pressure, such as heating systems, fuel systems, or industrial manufacturing setups.
 +86-576-82686004
+86-576-82686004
 allen@badavalve.com / daisy@badavalve.com
allen@badavalve.com / daisy@badavalve.com

 EN
EN
 Español
Español