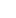
Press fit bronze elbow fittings are widely used in plumbing and piping systems for residential, commercial, and industrial applications. These fittings provide a reliable and durable way to connect two pipe sections at a 90-degree or 45-degree angle without the need for welding or threading. Their popularity is largely due to their corrosion resistance, ease of installation, and long service life.

Understanding the composition of a press fit bronze elbow is essential for ensuring its suitability for a specific application. The materials used, the design structure, and the functional components of the fitting all contribute to its overall performance. This article explores the typical composition of press fit bronze elbows, focusing on their material content, construction design, and operational function.
The primary material used in a press fit bronze elbow is bronze, which is a metal alloy primarily composed of copper and tin. In modern plumbing components, bronze often includes additional elements to improve specific properties such as strength, machinability, and corrosion resistance.
Copper forms the largest percentage of the bronze alloy, usually ranging between 80% and 90%. Copper provides the alloy with thermal and electrical conductivity, as well as strong resistance to corrosion. These characteristics make it ideal for water supply and heating systems, where the material is often exposed to varying temperatures and moisture.
Tin is the secondary element in bronze, typically making up 5% to 12% of the alloy. Tin contributes to the hardness and wear resistance of the material. It also helps improve the bronze's overall durability under mechanical stress, which is essential for pressurized plumbing systems.
To further enhance performance, small amounts of other elements may be added:
Zinc (Zn): Often included to increase strength and improve casting characteristics.
Lead (Pb): In controlled quantities, lead may be added to improve machinability, although its use is limited in potable water applications due to health regulations.
Phosphorus (P): Sometimes added to enhance wear resistance and reduce friction.
Nickel (Ni): May be used in specific bronze formulations to improve corrosion resistance in aggressive environments.
The exact composition depends on the intended use and the standards the fitting must meet. For potable water applications, lead-free bronze is commonly required in accordance with regulations such as NSF/ANSI 61.
The body of a press fit bronze elbow is typically formed through precision casting or forging processes, followed by machining to create a smooth and accurate surface for sealing. The elbow's shape can be a 90-degree or 45-degree angle, depending on the required pipe routing.
Key structural features include:
Smooth Interior Passage: Designed to minimize flow restriction and pressure loss.
Thick Wall Sections: To withstand internal pressure without deformation.
Reinforced Bend: The curvature of the elbow is strengthened to resist mechanical stress during installation and use.
After casting or forging, the fitting is often subjected to a heat treatment process to enhance its mechanical properties and ensure uniform material structure.
The defining feature of a press fit bronze elbow is the integrated press connection system, which allows the fitting to be joined to a pipe without soldering or threading. This system typically includes the following components:
A stainless steel or coated carbon steel sleeve is crimped onto the fitting's end. When pressed with a specialized tool, this sleeve deforms around the pipe to create a secure, leak-proof seal. Stainless steel is preferred in high-corrosion environments, while carbon steel offers a cost-effective option for general applications.
Inside the press sleeve is an elastomeric O-ring, usually made of EPDM (ethylene propylene diene monomer) rubber or other high-performance synthetic rubber. The O-ring ensures a watertight and airtight seal once the fitting is pressed.
The material of the O-ring may vary depending on the application:
EPDM: Suitable for hot and cold potable water.
FKM (Fluoroelastomer): Used for high-temperature or chemical-resistant applications.
HNBR (Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber): Suitable for oils and gases.
 +86-576-82686004
+86-576-82686004
 allen@badavalve.com / daisy@badavalve.com
allen@badavalve.com / daisy@badavalve.com

 EN
EN
 Español
Español