1. Connectors and Adapters
The major category of threaded bronze fittings includes connectors and adapters, which are primarily designed to join sections of pipe or connect pipes to equipment.

A coupling is a short fitting with internal threads on both ends, used to join two pipes of the same diameter. For instance, in residential plumbing systems, bronze couplings are often used to extend copper or brass pipelines carrying hot water. Their corrosion resistance makes them especially useful in systems exposed to moisture or variable temperatures. Some couplings also come in “reducer” forms, allowing the connection of pipes with different diameters.
A union serves a similar purpose but offers the added advantage of easy disconnection. It consists of three parts: two threaded ends and a central nut that allows the joint to be separated without rotating the pipes. This feature is practical in installations where regular maintenance or inspection is required, such as in pump connections or heating systems. A common example can be found in ship engine rooms, where unions are used to connect water circulation pipes to pumps, enabling fast disassembly during servicing.
A bushing is another type of connector, used to join pipes of different thread sizes. It has male threads on the outside and female threads on the inside. For example, when adapting a large pipe to a smaller outlet in a bronze valve, a bushing provides the necessary transition without requiring major modifications to the system. Bushings are frequently used in irrigation systems or small industrial machinery where thread compatibility between components varies.
These fittings highlight the role of connectors and adapters in ensuring system compatibility and flexibility. Their threaded design allows for simple installation, and the bronze material ensures durability in demanding conditions.
2. Directional Fittings
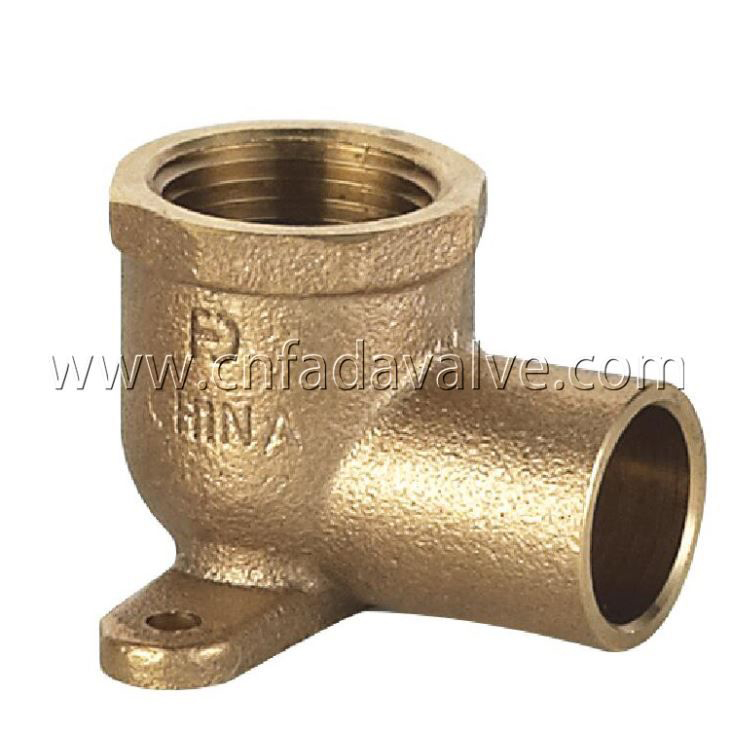
The second category includes directional fittings, which alter the flow direction of the fluid or connect pipes arranged at different angles. Common examples include elbows, tees, and cross fittings.
Elbows are among the widely used directional fittings. They typically come in 45-degree or 90-degree angles and are threaded on both ends. In building plumbing systems, 90-degree bronze elbows are often used to route water lines around corners or obstacles. For example, in commercial kitchens where space is limited, elbows allow the water supply line to fit neatly along the wall while maintaining flow efficiency. The strength of bronze prevents deformation even under high water pressure, ensuring consistent performance.
Tees have one inlet and two outlets (or vice versa) arranged in a T shape, allowing for the division or combination of fluid flow. Threaded bronze tees are common in compressed air lines or fuel systems, where one line must split into two directions. In fire suppression systems on ships, for instance, tees distribute water from the main line to branch outlets nozzles or hydrants. This configuration provides balanced distribution while maintaining structural integrity.
Cross fittings, which have four openings, serve to connect four pipes meeting at a single point. Although less common than elbows or tees, they are useful in complex piping networks, such as industrial cooling systems or water treatment facilities. The threaded connection simplifies installation and allows quick changes in configuration if the system layout needs adjustment.
Overall, directional fittings play a key role in determining the geometry of the piping system. By controlling how fluids travel through different sections, they contribute to both the efficiency and safety of the entire installation.
3. Control and Closure Fittings
The third category of threaded bronze fittings includes control and closure fittings, which manage or terminate the flow within the system. The common types are plugs, caps, and valves.
A plug is a solid fitting with external threads, used to close the end of a pipe or fitting. Plugs are frequently employed in maintenance operations, where a section of the pipeline must be sealed temporarily or permanently. For example, in a marine ballast water system, plugs may be used to close inspection openings when the system is not in use. Their threaded design allows for quick removal during future maintenance.
A cap performs a similar function but differs in having internal threads that fit over the external threads of a pipe. In household water systems, bronze caps are often used to seal unused outlets, such as spare connections in a plumbing manifold. Because they can be easily removed, they provide flexibility for future system expansion.
Valves, while more complex, also belong to this category because they regulate or stop flow within a threaded system. Bronze ball valves or gate valves with threaded ends are common in domestic water lines, small irrigation systems, and industrial fluid control networks. For example, a threaded bronze valve can be installed at the outlet of a water tank, allowing precise control of discharge. The corrosion resistance of bronze ensures consistent operation even when exposed to moisture or chemicals.
These control and closure fittings provide essential functionality for operation and maintenance. They help isolate, shut off, or reroute sections of a pipeline safely and efficiently.
 +86-576-82686004
+86-576-82686004
 allen@badavalve.com / daisy@badavalve.com
allen@badavalve.com / daisy@badavalve.com

 EN
EN
 Español
Español